Columns on Access Control/Face Recognition
What is Biometrics Authentication?
Types and Features


Breadcrumb navigation
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Authentication is used in a variety of situations, such as system logins and building entry/exit. Authentication is an indispensable technology in business as a means of preventing unauthorized intrusion and protecting critical information. In this article, we will explain the overview, types, benefits that can be obtained, and the issues that arise about "biometric authentication," which has been attracting attention in recent years due to its security robustness, among authentication technologies.
1. What is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication (biometrics) is an advanced technology that uses body-related elements for authentication. It involves pre-registering identifiable information such as facial features, fingerprints, voice, and veins into the system, and then verifying if these physical characteristics match those of the individual. Since each person’s body is unique, biometric authentication is more secure and harder to spoof compared to other methods like password authentication. This makes it widely used in scenarios requiring high security, such as financial institutions. However, the implementation cost is often higher compared to other authentication methods.
A common example is the use of facial recognition or fingerprint recognition to unlock smartphones. In recent years, there have been numerous incidents of data breaches and service disruptions due to unauthorized access, highlighting the necessity of robust authentication methods to enhance security.
2. Types and Features of Biometric Authentication
There are three main types of information used for authentication: “knowledge information,” which includes passwords and PIN codes known only to the individual; “possession information,” which includes items such as IC cards and smartphones that only the individual possesses; and “biometric information,” which uses the individual’s physical characteristics. In addition to well-known elements like facial features and fingerprints, biometric authentication can also use iris patterns and DNA. This section explains the characteristics of each type, the benefits they offer, and the concerns associated with their use.
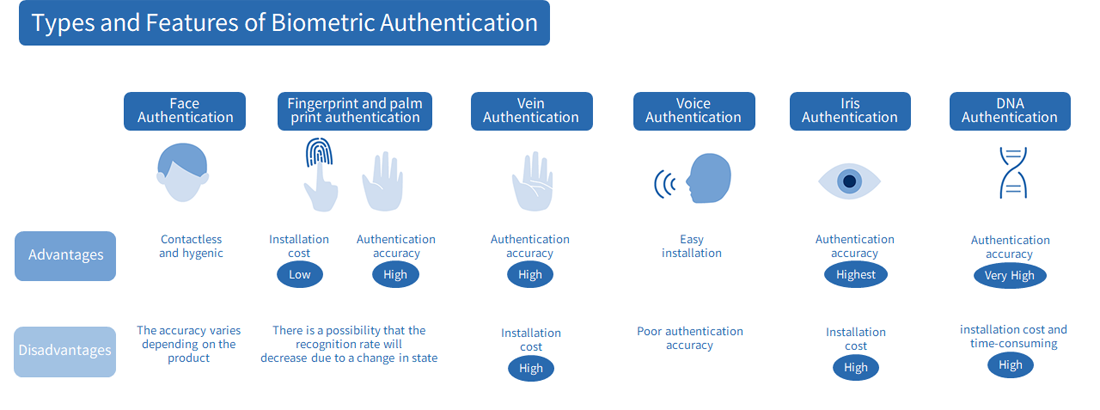
Face Authentication
Face recognition is a method of authentication that uses features of the face, such as the contour, eyes, nose, and mouth. It involves analyzing the characteristics of an individual’s face from photos or videos taken in advance, and then matching the face captured by the camera during authentication with the stored facial features.
Since it can authenticate just by capturing an image with a camera, it is contactless and hygienic. Additionally, it only requires the user to face the camera, which reduces psychological burden. However, the accuracy can vary between products, and some may not authenticate if the user is wearing glasses or a mask, or if the face has changed over time. When implementing facial recognition, it is recommended to check the features of each product and compare them to see if they meet your operational needs.
An example of a product that can perform facial recognition even when wearing a mask is “Bio-IDiom KAOATO,” a facial recognition package software provided by NEC Solution Innovators, Ltd.
“Bio-IDiom KAOATO” performs facerecognition upon entry, preventing unauthorized access and enabling contactless door unlocking. It is a facial recognition package software equipped with the world's No. 1* rated face recognition engine, achieving high authentication accuracy.
- *
 No. 1 in face recognition benchmark testing by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) multiple times to date. (Japanese text only)
No. 1 in face recognition benchmark testing by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) multiple times to date. (Japanese text only)
NIST evaluation results do not constitute an endorsement by the U.S. government of any particular system, product, service, or company.
Fingerprint and Palmprint Authentication
Among biometric authentication methods, fingerprint recognition was one of the earliest to be put into practical use. Fingerprints refer to the patterns formed by the ridges on the fingertips, which vary from person to person and even from finger to finger. Due to their unchanging nature over a person’s lifetime, fingerprints have been used for managing criminal records since the 19th century. With technological advancements, the miniaturization and cost reduction of systems have made fingerprint recognition widely adopted in personal devices such as computers and smartphones.
Fingerprint recognition involves extracting and storing characteristic points from pre-registered fingerprint data, and then matching this information with the fingerprint data obtained by the sensor during authentication. Due to its relatively low implementation cost and high accuracy, fingerprint recognition is also being adopted for cardless payment services in stores. However, it is important to note that the recognition rate can decrease due to sensor errors caused by dirt or scratches, or changes in the condition of the fingers, such as dryness in winter or wrinkling after a bath.
Palmprint recognition, on the other hand, uses the entire palm’s pattern (ridge pattern) instead of fingerprints. Since the reading area is larger than that of fingerprints, larger sensors are required.
Vein Authentication
Vein recognition is a method of authentication that uses the pattern of veins in the back of the hand or fingers. It leverages the property that hemoglobin in the blood absorbs infrared light, making the veins appear dark. The system extracts the distribution pattern from pre-registered vein information and matches it with the vein pattern read by an infrared sensor during authentication. While it offers high accuracy, the significant implementation cost is a challenge.
Voice Authentication
Voice recognition is a method of authentication that analyzes a person’s voice. Since each person’s voice has unique characteristics due to the shape and size of their vocal organs and articulation, it is used as authentication information. The advantage of voice recognition is that it can be processed with a standard computer and microphone, making it easy to implement. However, compared to vein recognition, it has lower accuracy and can be spoofed with recordings. To address the accuracy issue, multi-factor authentication is recommended.
Iris Authentication
Iris recognition is a method of authentication that uses the iris of the eye. The iris is the donut-shaped part of the eye excluding the pupil. The iris pattern is unique to each individual and differs between the left and right eyes. Since the pattern stops changing a few years after birth, it is advantageous for authentication. Among biometric authentication methods, iris recognition offers the highest accuracy and is difficult to forge, but the implementation cost may be a concern.
DNA Authentication
DNA recognition is an authentication method that uses the unique base sequence of human DNA. DNA is widely known as an accurate identifier, often used in criminal investigations. Unlike other biometric authentication methods that analyze and extract features for pattern matching, DNA can be directly compared. Cells are collected from the oral cavity or other areas, and DNA is extracted and analyzed to generate a “DNA-ID” as identification information. During authentication, the individual’s DNA is analyzed, and if the same DNA-ID is generated, it confirms the identity. While DNA recognition offers extremely high accuracy, it requires significant time and cost, limiting its use to special applications at present.
3. Installation Benefits of Biometric Authentication
Compared to traditional authentication methods like ID/passwords or IC cards, biometric authentication offers several advantages. Below, we explain the benefits of biometric authentication, including robust security, high convenience, and fast verification.
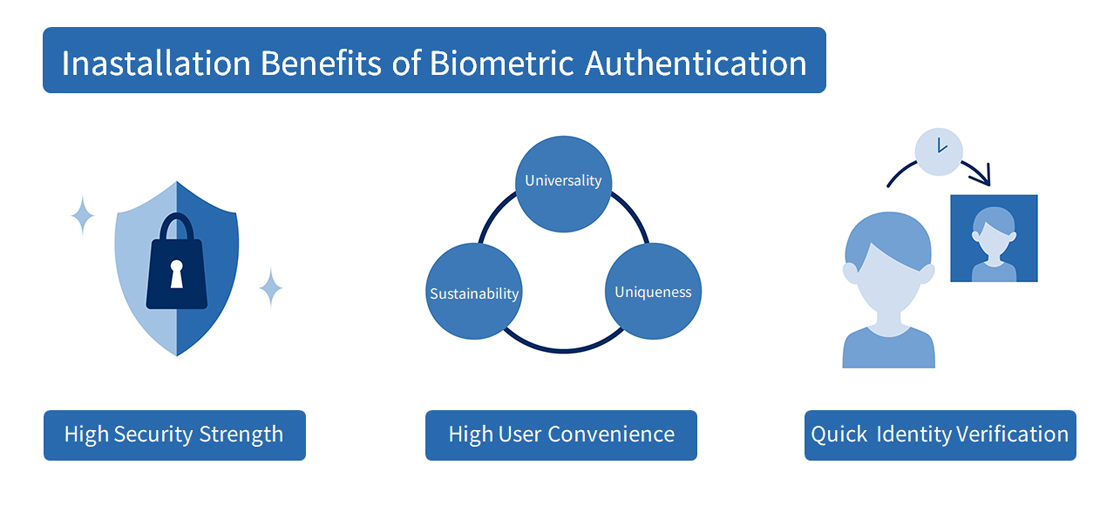
High Security Strength
In authentication, the probability of mistakenly accepting someone else as the individual is called the “False Acceptance Rate (FAR).” Biometric authentication is expected to have a low FAR due to its high security. Additionally, unlike passwords, even if the information is leaked, it is difficult to spoof, which significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
High User Convenience
Biometric information has the characteristics of “universality,” meaning everyone possesses it; “uniqueness,” meaning no one else has the same features; and “permanence,” meaning it does not deteriorate over time and remains unchanged throughout life. Therefore, there is no need to carry physical media like IC cards or input and manage information like IDs and passwords during authentication. The lack of complex operations and the ability to complete authentication instantly contribute to its high convenience.
Quick Identity Verification
Biometric authentication shortens the time required for authentication by analyzing and registering the necessary features in advance. For example, in facial recognition for entry and exit, simply facing the camera while passing by is sufficient, allowing for smooth and congestion-free authentication.
4. Issues on Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication offers many advantages compared to other authentication methods. However, it also presents unique challenges, such as the need to handle personal information with care and to address changes in biometric data due to various conditions. Additionally, it is important to understand that biometric authentication cannot completely prevent spoofing.
Need for Careful Handling as Personal Information
Biometric information, such as fingerprints and DNA, qualifies as personal information that can uniquely identify an individual. Since this information does not change over a person’s lifetime, any leakage can lead to significant issues. Therefore, strict management, such as encryption, is necessary when storing this information in systems. Some individuals may also have concerns or objections from a privacy perspective about recording and using their biometric information in systems. It is crucial to communicate clearly about the purpose of data use and to explain that the system stores not the biometric information itself but the features used for matching, to alleviate users’ concerns.
It's not completely unexploitable by others
It is not completely immune to misuse by others While it is extremely difficult to steal or forge biometric information, it is possible for others to obtain fingerprints or voice data, making impersonation a potential risk. There have been instances where fingerprint recognition was bypassed using fake fingers made of gelatin, and security experts have pointed out the risk of reproducing fingerprint information from high-resolution photos.
Additionally, some voice recognition systems can be spoofed, and there are cases where identical twins have been misidentified.
When implementing biometric authentication systems in a company, it is important not to overestimate the security provided by biometrics. Some systems include AI features that use additional information, such as temperature, to prevent spoofing. It is advisable to compare systems with these features. Also, since biometric authentication uses physical information, it is difficult to change the authentication information immediately if biometric data is stolen, unlike passwords.
Necessary to deal with changes in biometric information
As mentioned earlier, biometric information is characterized by its permanence, but recognition rates can decrease under certain conditions. For example, facial recognition may be affected by plastic surgery, aging, the presence of glasses or masks, and lighting conditions. Fingerprint recognition may be influenced by dryness or wear.
Therefore, it is prudent to have additional authentication methods in place, such as using a PIN code if facial recognition fails, to ensure proper authentication.
5. Summary
Biometric authentication refers to the use of an individual’s physical information, such as facial features, fingerprints, and veins, for authentication. Due to its high accuracy and convenience, it is increasingly being implemented not only on its own but also as part of multi-factor authentication combined with password authentication. While biometric information offers various advantages, it also presents challenges, such as the need for strict management of personal information and higher costs compared to other authentication methods. When companies consider implementing biometric authentication as a security measure, it is important to compare and evaluate the methods and systems based on accuracy, cost, convenience, and operational efficiency.
For example, in building access management, convenience and low cost, allowing many people to enter and exit smoothly, are often prioritized over high confidentiality restricted to a few individuals. In such scenarios, facial recognition is recommended due to its ease of implementation with cameras, contactless and instant authentication, and relatively high accuracy.
NEC Solution Innovators, Ltd., part of the NEC Group, offers the facial recognition package software “Bio-IDiom KAOATO.” Leveraging over 10 years of development expertise, it features numerous functions required for practical use, such as preventing forgery with photos, simultaneous authentication of multiple people, and continuous operation during communication failures. Its ease of use and high convenience for administrators have been highly evaluated, with over 1,500 installations worldwide, including in visitor management systems.
The Reason that Face Recognition is chosen for Access Control
Here is a detailed explanation of why face recognition is chosen for access control, and why Bio-IDiom KAOATO is chosen among them. Please take a look.
Please consider adding "Bio-IDiom KAOATO" developed by NEC Group, which boasts a deep reputation for facial recognition technology, as one of your options.
“Bio-IDiom KAOATO” performs face recognition upon entry, preventing unauthorized access and enabling contactless door unlocking. It is a facial recognition package software equipped with an industry-leading facial recognition engine, achieving high authentication accuracy.

